A New Vision for ASM
We support a well-regulated ASM sector that contributes to poverty reduction, safeguards the environment, and delivers shared benefits - especially women and local communities.
ASM is a vital and growing part of national development and international trade. In 2024, over 315 million people across Africa, Asia and Latin America depended on ASM for their livelihoods. Around 45 million people work directly in mining, with women representing between 18% to 50% of the workforce, depending on the country and commodity. ASM covers a wide range of minerals—from gold, cobalt, and copper to salt, gravel, and gemstones. Its share in the global mineral supply chains is increasing.
The World Bank works to professionalize ASM by supporting job creation, improved livelihoods, and stronger revenue streams. This involves building local systems for legal, well-managed mining, improving environmental and social practices at mine sites, expanding access to finance, and strengthening local trade. Governments play a critical role in guiding and growing the sector, while both miners and institutions alike are encouraged to adopt standards that raise practices and governance across the sector.
Improving ASM requires a shift in mindset—from viewing it primarily as a risk to recognizing its potential to generate jobs, create wealth, and and support national development. Achieving this shift depends on stronger data, better research evidence, and smarter program design that enable evidence-based policies and scalable solutions.
Creating a new unifying narrative for ASM

Our Framework of Engagement reflects the priorities identified by ASM stakeholders: improved incomes, safer working conditions, and stronger environmental stewardship.
The framework is structured around two pillars – legitimacy and professionalization – with nine intervention areas. Legitimacy emphasizes the of government in creating the enabling policies, institutions, and governance systems that foster legal, transparent and well-regulated ASM. Professionalization focuses on strengthening the skills, practices, and capacities of miners and institutions to raise productivity, improve environmental and social performance, and meet legal and governance standards. The Framework recognizes supporting ASM requires that an integrated approach. It also underscores three cross-cutting themes - scale, digital solutions and partnerships – as critical to advancing sustainable and inclusive outcomes for the ASM sector.
ASM Framework
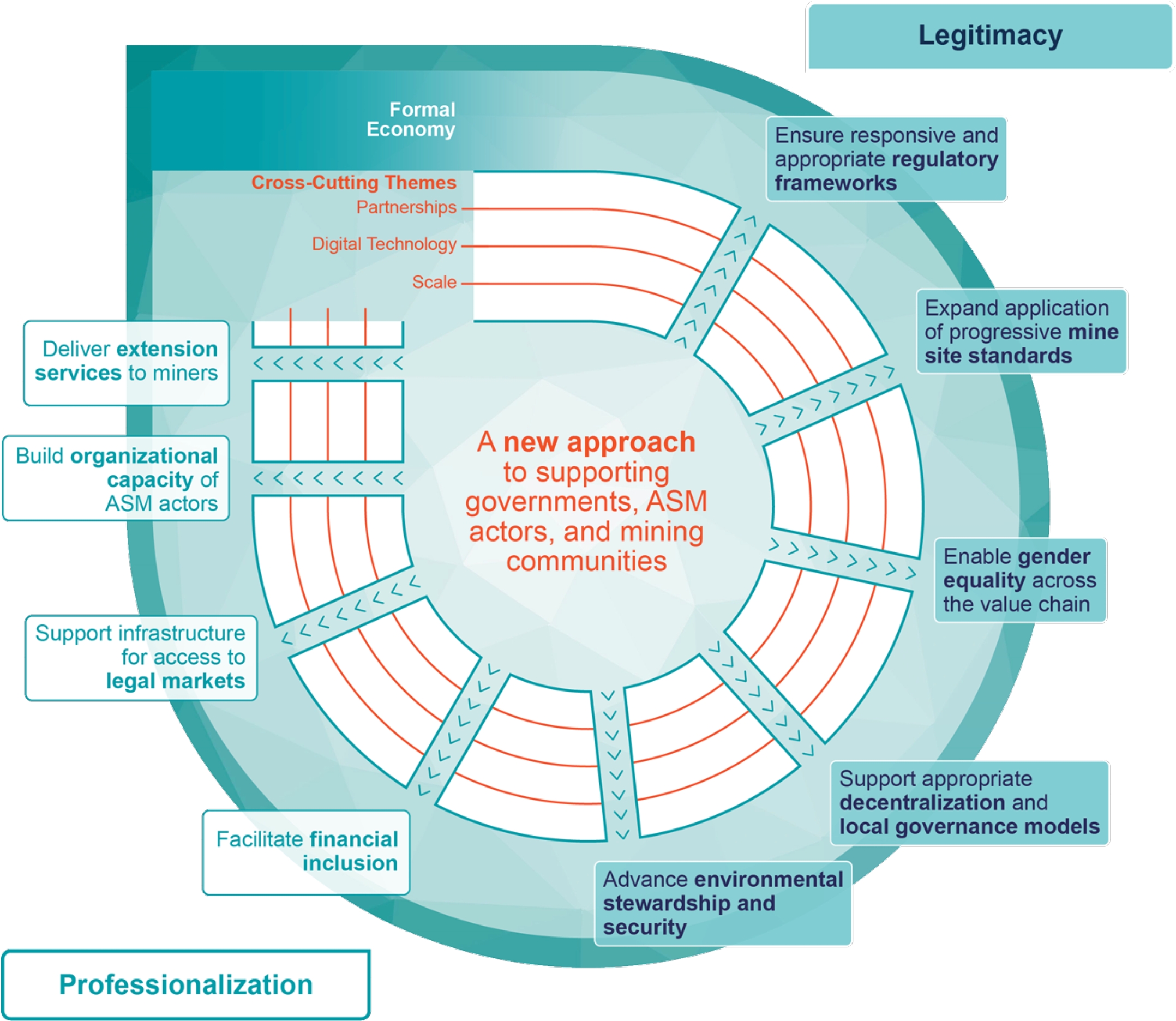
Priority Engagements
The Multistakeholder Partnership Initiative for Sustainable and Responsible Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold (ASGM) Mining
Background

In 2023, the World Bank and the World Gold Council launched a partnership to promote sustainable and responsible artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM). They combined their strengths—like development know-how, funding, market insights, and strong networks—to support this goal. The partnership focuses on helping governments improve gold mining through better infrastructure, security, and conflict resolution. It also aims to bring in more partners, including large gold mining companies, development agencies, investors, and others involved in the gold supply chain.
Objectives
The MSPI aims in selected countries to:
Support Governments and ASM Entities
Nurture sustainable small-scale gold mining sectors in select countries.
Promote Legal and Responsible Mining
Ensure small-scale gold mining leads on environmental and social stewardship.
Foster Collaboration
Encourage host governments, large-scale mining (LSM) companies, ASGM actors, civil society and other technical partners to work together under a common governance framework.
Mitigate Security Risks
Address governance and security risks posed by illicit gold flows.
Encourage Sustainable Mining Practices
Promote climate-smart mining, gender equality, and mercury-free technologies.
Vision

By 2033, small-scale gold mining will contribute positively to national development by collaborating with governments, the private sector, and downstream supply chain actors to mine and sell gold legally and sustainably in the international market.
Scope and Phases
The MSPI will be implemented in two phases:
Phase 1 (2023-2025)
Establish national MSPI structures and pilot model small-scale gold mines in select countries of West Africa and Sahel.
Phase 2 (2026-2033)
Scale out the model to other countries and regions, deepen regional learning through regular in-person exchanges and peer-to-peer forums-, and ensure sustainability.
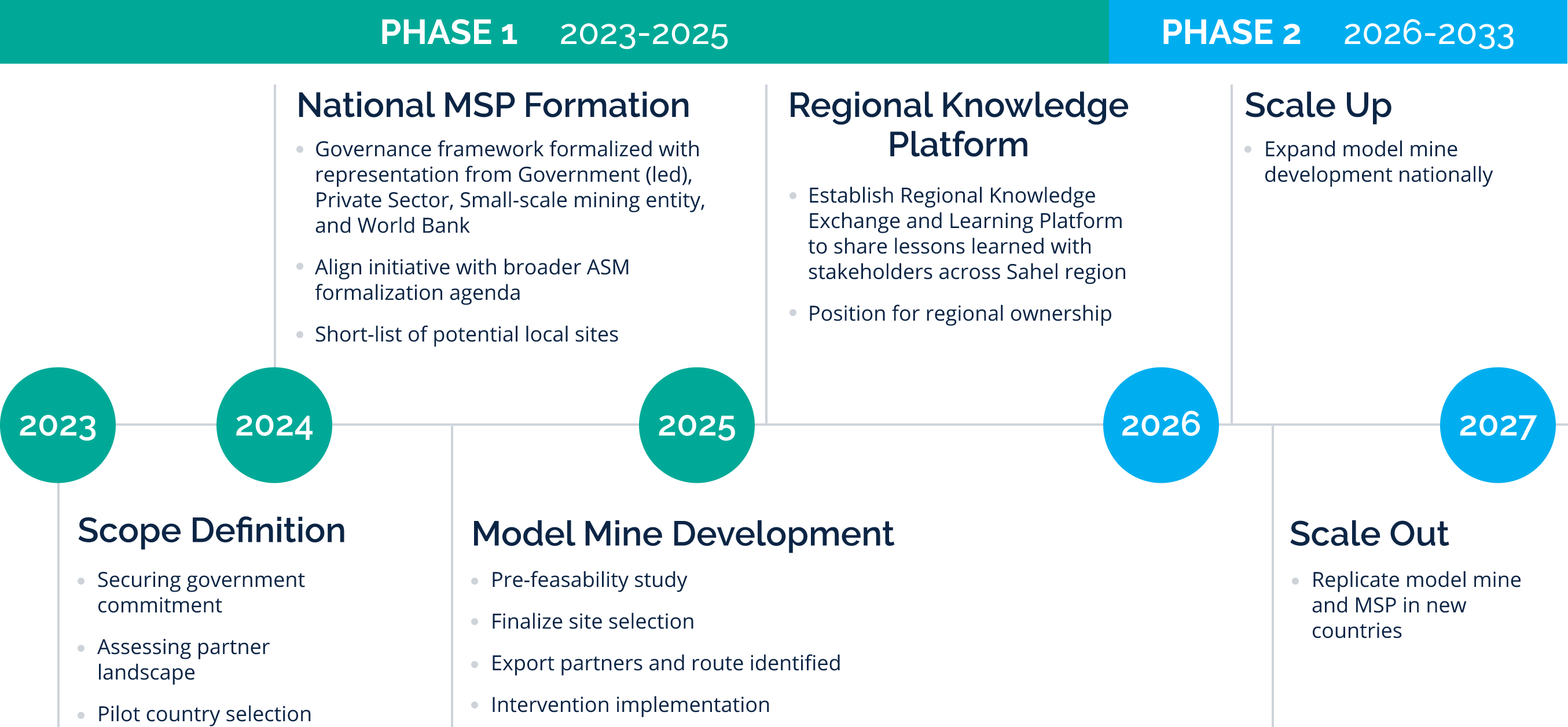
Key components
Building Partnerships
- Leadership and Governance: Establish formal agreements involving host country governments and institutions, mining companies, the World Gold Council, the World Bank, and small-scale miners.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Ensure representation and transparent communication across all mining sectors.
- Governance Framework: Define clear roles and responsibilities, focusing on community and government involvement.
Creating Model Mines
- Collaboration: Governments, small-scale miners, large-scale operators and formal downstream actors work together to develop sustainable model mines.
- Support and Training: Mobilize technical expertise, financial aid, and training for small-scale miners on best practices and guide their output to the formal bullion market.
Sharing Knowledge Regionally
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitate in-person exchanges, study tours, and regional learning events to share best practices in sustainable and responsible ASM
- Regional Forums: Convene regular gatherings of key ASM stakeholders to promote dialogue, collaboration and joint problem-solving.
Monitoring and Scaling Up
- Evaluation Framework: Implement a system to monitor progress and adapt quickly.
- Risk Management: Develop strategies to address and mitigate risks in the unregulated market.
2) The World Bank defines sustainable artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) as mining activities that align with the United Nation’s sustainable development principles. Sustainable ASM focuses on improving miners' incomes and security, ensuring that practices align with national legislation and international best practice, enhancing occupational health and safety, and promoting environmental stewardship.
3) The World Gold Council defines responsible gold industry practices as those that operate responsibly and sustainably from mine to market, maintain public trust, and support socioeconomic progress. Key principles include aligning with responsible sourcing standards, advancing the UN Sustainable Development Goals, respecting human rights and core labor standards, promoting diversity and inclusion, considering impacts on indigenous peoples and vulnerable populations, addressing climate change, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Delve and Delve Exchange
Delve is the World Bank’s global platform on artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM), established in 2016 as the primary public digital resource for ASM data, research and insights. It hosts reports, datasets, and tools, and produces the flagship State of the ASM Sector report (2019, 2020, 2023) tracking ASM’s contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

The World Bank intends to continue:
- Growing the platform’s data and resources
- Building strategic partnerships for data sharing and financial sustainability
- Enhancing external communications and platform user experience
- Producing the initiative’s flagship State of the ASM Sector report
Delve Exchange began in 2021, as the platform’s miner-led, peer-to-peer engagement arm. It connects over 3,000 miners and quarry workers from 71 countries through six regional WhatsApp groups and regular forums, providing a space to share knowledge, solve problems, and surface local innovations. This network of miners worked alongside regional academic partners to co-create the ASM Academy, an online learning program created with miners for miners to encourage safer and more responsible practices at mining sites and includes topics such as:

The next phase will integrate Delve and Delve Exchange into a single, more interactive and sustainable hub that combines global data, knowledge products, and miner-led engagement in one place. Priorities include:
- Expanding and improving ASM data, resources, and reach
- Continuing the State of the ASM Sector as the platform’s flagship publication
- Integrating community engagement tools directly into the Delve platform
- Ensuring the miner voice remains central to shaping ASM’s future
Mining.Better.Together
Mining.Better.Together is a global call to improve environmental and social performance at artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) sites – across all commodities – and to deliver greater benefits for miners, their families and their communities.
ASM is a vital source of income for over 315 million people but often takes place in informal, unsafe, and environmentally damaging conditions. Too many miners work without legal protections, fair market access, or the means to adopt safer, more sustainable practices. With growing demand for responsibly sourced minerals and renewed government commitment to professionalizing the sector, there is a unique opportunity to raise the bar together.

Led by the World Bank, Mining.Better.Together is being shaped in consultation with key ASM stakeholders worldwide to ensure it reflects local realities and global ambition. It represents a new way of working together to expand proven good practices and foster responsible investment in ASM supply chains. It is :
- A Movement – a shared commitment uniting miners, women’s networks, NGOs, companies, buyers, and governments.
- A Convenor – connecting partners, knowledge, and action for greater impact.
- A Facility – mobilizing finance and technical support to scale solutions and improve ASM sites worldwide.
Partnerships
The World Bank aims to be a valued partner in ASM at national, regional, and global levels. Following the One World Bank Group Partnership Charter, it supports countries in leading their own development plans while working with other key partners —like the private sector, civil society, and nongovernmental organizations. By fostering collaboration, mutual learning, and alignment across partners, the World Bank helps generate scalable and sustainable development solutions.
Partnerships take many forms and support a range of activities:
The World Bank uses recent experiences to shape partnership models with key stakeholders.
To maximize impact, the World Bank will also strengthen collaboration across its institutions —IBRD, IDA, IFC, and MIGA. Together, these partnerships will expand financial access, advance gender equality, support small business growth, and strengthen local trade in the ASM sector. By combining the World Bank’s development expertise, IFC’s private investment tools, and MIGA’s investor guarantees, the institution can deliver comprehensive support for ASM.

